What Is Industrial Radiography Used For?
Radiography is the process of using radiation to generate images of objects that cannot be seen directly with the naked eye. In the medical field, radiography helps create images that reveal conditions inside the human body, such as bones, tissues, or internal organs. In industrial settings, radiography serves as a crucial tool for detecting flaws that might not be visible during regular inspections.
This guide will delve into the various applications of industrial radiography across different industries, focusing on its role in supporting inspections. If you're interested in learning about how radiography is used in medical contexts, we recommend checking out this article by the FDA.
[Industrial radiography is just one of the non-destructive testing (NDT) methods that inspectors rely on. To learn more about NDT, explore this comprehensive guide.
[Note: Industrial radiography is also sometimes referred to as industrial radiology.]
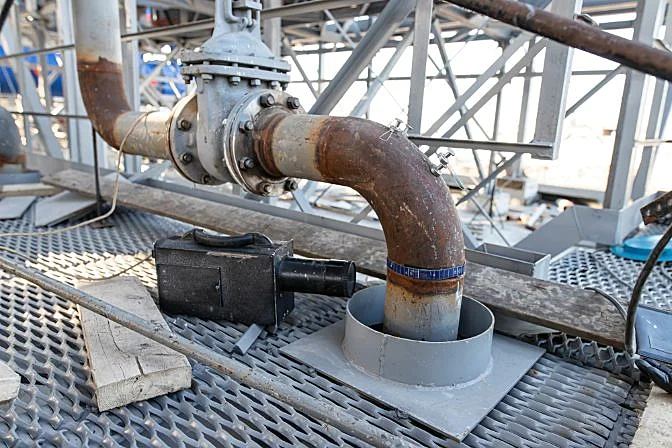 Radiographic testing applied to a pipe
Radiographic testing applied to a pipe
Industrial Radiography
Industrial radiography (IR) involves using radiation to assess the structural integrity and condition of materials. Both gamma rays and x-rays are utilized in industrial radiography, as these forms of radiation can penetrate many substances, enabling inspectors to examine the internal structure of materials without altering them.
Industrial radiography serves two main purposes:
-
Manufacturers use industrial radiography to identify defects within the materials they use. This ensures that components meet quality standards before they are incorporated into products.
-
Inspectors employ industrial radiography to check for defects in industrial assets, ensuring their safety and compliance with mandatory inspection requirements.
Industries such as automobile and aircraft manufacturing commonly use radiographic testing to inspect vehicle and plane parts. In the realm of inspections, industries dealing with boilers, welding, and pipelines, including Oil and Gas and Power Generation, frequently utilize radiography.
[Related read: What Is a Dosimeter and Why Is It Important?]
 An industrial boiler
An industrial boiler
Non-Destructive vs. Destructive Testing
Inspection methods like radiography, which allow inspectors to examine materials without altering them, are termed non-destructive testing (NDT) methods due to their non-invasive nature. In contrast, destructive testing methods involve taking samples or altering substances to gather information.
For instance, if you want to confirm whether lead is present in paint, a simple chemical test that changes color upon encountering lead could be used. However, this method permanently alters the paint, classifying it as a destructive testing technique.
A Note on Safety in Industrial Radiography
The radiation used in industrial radiography originates from either a radiation-producing machine or a radioactive material source. While industrial radiography is a powerful tool for assessing the internal structure of materials, it poses risks if not handled properly. Compared to other radiation-related work, industrial radiographers face the highest risk of radiation-related accidents.
Due to these hazards, strict procedures are in place, often regulated by law. For more information, refer to the Careers and Salary section below.
Radiographic Testing—How Does It Work?
Radiographic testing involves using radiation to inspect or test materials for inspection purposes. Here's how it works:
-
Align Radiation Source. Inspectors direct radiation (either gamma rays or x-rays) towards the object being inspected.
-
Position Detector. On the opposite side of the object, the inspector places a detector aligned with the radiation beam.
-
Record Data. The detector records the radiation passing through the object.
-
Analyze Results. The recorded data is analyzed to determine the findings from the test.
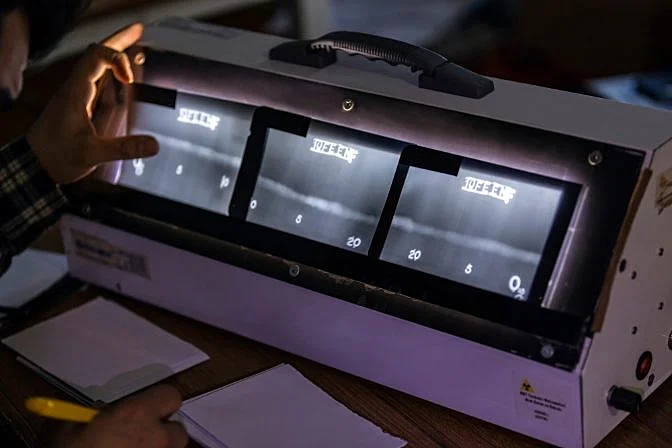

At a high level, industrial radiographers look for areas where less or more radiation passes through the object during analysis. Less radiation indicates thicker material, suggesting it's in good condition. Conversely, more radiation suggests thinner material, possibly due to cracks or flaws.
The images produced from radiographic testing are known as radiographs. Nowadays, most cameras used for radiography capture digital images, though earlier methods used film.
Industrial Radiography Equipment
Two primary types of industrial radiography equipment exist, each utilizing a different form of radiation: x-rays and gamma rays.
Gamma Rays Industrial Uses & Equipment
Equipment using gamma rays contains radiation sourced from radioactive materials within the device. Such equipment is compact, making it ideal for use in smaller spaces. However, it cannot be turned off and constantly emits radiation. To safeguard workers, it must be enclosed in a specially designed metal casing.
X-Rays Industrial Uses & Equipment
Equipment using x-rays is typically larger, making it suitable for radiographic testing in expansive environments like factories or warehouses. X-ray equipment operates on electricity and can be powered on or off, meaning it's safe to be around when off (no protective shielding is necessary).
Given the potential dangers of radiation, the use, ownership, and transport of radiography equipment require licensing in the U.S. and several other regions. In the U.S., the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission creates and oversees licensing regulations. Learn more here.
Industrial Radiographer Salary and Careers
Interested in becoming an industrial radiographer? Here's what you'll need:
-
A high school diploma
-
Certification from an industrial radiographer training program
What is an Industrial Radiographer?
An industrial radiographer employs radiation to conduct tests on materials, equipment, and assets to determine their integrity or presence of flaws. For asset inspections, industrial radiographers often examine large items like aboveground and underground pipelines, typical in the Oil and Gas industry, or other large machinery.
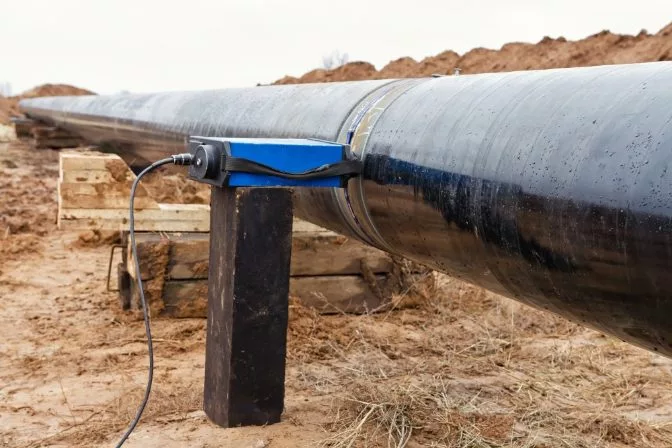 Radiographic testing applied to a weld in an aboveground pipe
Radiographic testing applied to a weld in an aboveground pipe
To perform this work, industrial radiographers create images using x-rays and analyze them for defects or flaws. During this process, they must adhere to safety protocols to minimize radiation exposure.
Jobs in industrial radiography are typically full-time, requiring travel to job sites since the objects being tested are usually large, stationary assets that need on-site inspections.
What Does an Industrial Radiographer Salary Look Like?
According to ZipRecruiter, the national average industrial radiographer salary is approximately $54,000 annually. Here are salaries from the top-paying industrial radiography jobs in the U.S.:
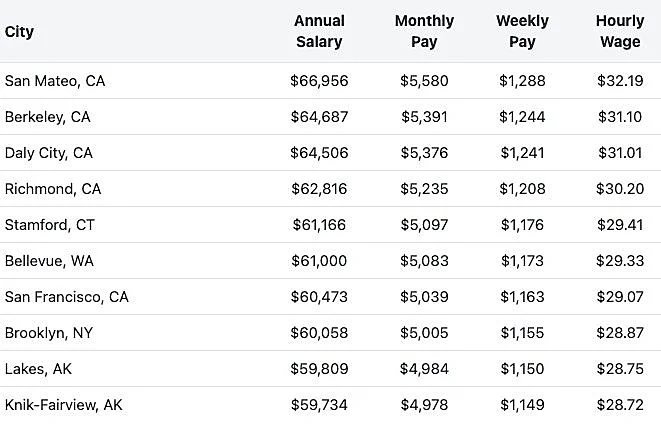 Data provided by ZipRecruiter
Data provided by ZipRecruiter
As noted, your salary may vary based on your location. Additionally, inspectors might earn more—and sometimes significantly more—by acquiring additional certifications and experiences that enable them to conduct other types of inspection work.
Industrial Radiography Certification
In the U.S. and many other regions, certification is essential for performing industrial radiography work. Certification requirements differ between states and countries, but they typically include:
-
Hands-on training for a specified number of hours under a certified industrial radiographer
-
Completion of a radiation safety course
-
Passing a written examination
Common certification types include:
-
RAM: Certification solely for radioactive materials.
-
X-RAY: Certification solely for x-ray machines.
-
Both: Certification for both radioactive materials and x-ray machines.
In the U.S., several states have their own nationally recognized IR certification programs. Learn more here.
As technology advances, we may soon be able to produce full, highly detailed 3D models of the interiors of assets. These models could serve as visual records for monitoring corrosion in assets, much like high-quality still images and videos do today.
Drones and Industrial Radiography
Although drones aren't widely used in industrial radiography yet, this could change in the coming years. Currently, there is at least one drone, the DroneX by Pacific Imaging, equipped with an x-ray imaging system.
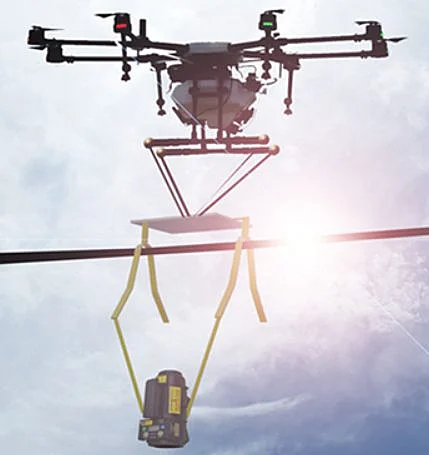 Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
Photo credit: Pacific Imaging
Our research shows that the DroneX platform is already being used for power line inspections, enabling inspectors to gather data about the condition of power lines without putting themselves at risk by climbing or standing in a bucket truck for manual inspections.
As drone technology continues to evolve, we may see more drones equipped with x-ray imaging capabilities, expanding the possibilities of industrial radiography.
There are many products classified in this section of Automatic Paper Attaching. They are focused on folding all kinds of garments with Automatic Paper Attaching. Attention: The following garment are applied to this auto folding packing machine. Like, garment designed with many accesories, too thick coat,suits t shirts.
All machine include the following function:
1.Within the allowable value range, the folded length and width can be adjusted as you want.
2.The machine can automatically detect the length of garment, when the garment size is different, machine can intelligently identify and automatically fold according to the first folding length, so as to ensure the uniform folding length without changing the polybag. Clothes of different sizes can be folded into uniform sizes and packed into bags.
3.Machine will calculate the number of completed pieces automatically, and the alarm function for multiple
garments can be set up.
Clothing Folding Machine, Hoodies Folding Machine, Automatic Clothes Folder, Automatic Clothes Machine
SHENZHEN LINGCHUANG ZHUOYUE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD , https://www.lcautosz.com